Pineal Gland Tumors
Pineal region tumors:
- WHO Grade I: Pineocytoma
- WHO Grade (): Pineal parenchmal tumor of intermediate differentiation
- WHO Grade IV: Pineoblastoma
Epidemiology
Pineal region tumors account for about 2% of intracranial pediatric tumors. About half are germ cell tumors and 1/4 are pineal parenchymal tumors, with the balance being predominantly astrocytic tumors. Pineal cells are photosensory and neuroendocrine in nature.
Pathology and Natural History
Pineocytomas are slow growing and composed of small uniform mature cells with occasional large pineocytomatous rosettes. They account for about half of the childhood pineal parenchymal tumors in kids. They are most commonly diagnosed in teenage years. The typical presentation is increased intracranial pressure. Some will present with Parinaud's Syndrome due tomesencephalic tegmental dysfunction which is manifest in a continual upward gaze, lid retraction, retraction nystagmus, and poorly reactive pupils, while preserving reaction to accomodation.
Clinical Workup and Evaluation
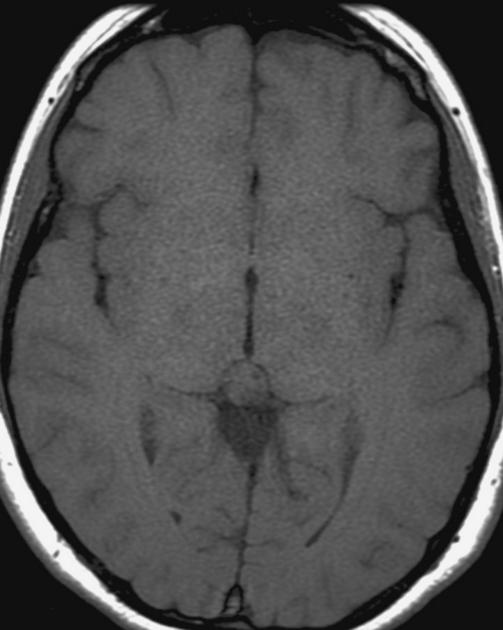
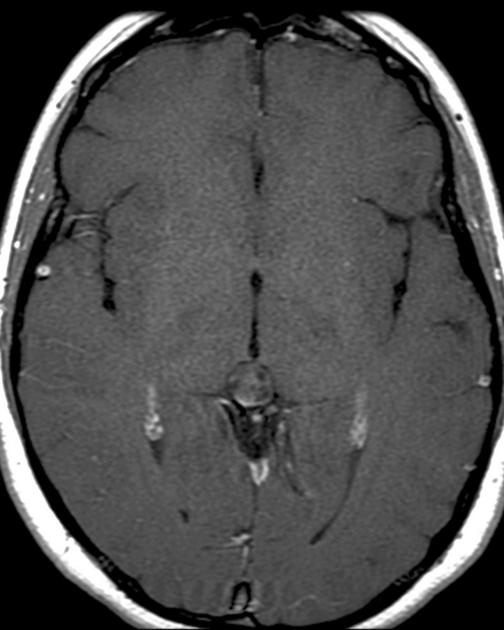
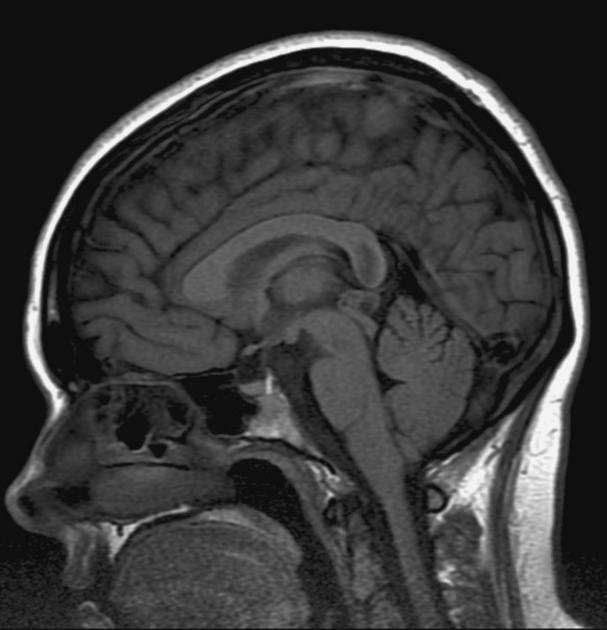
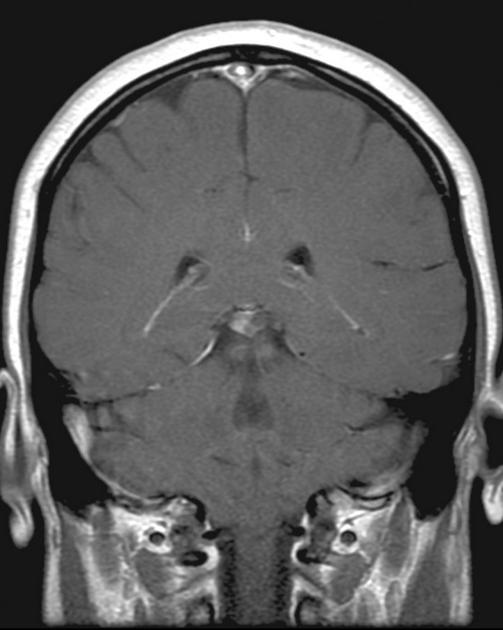
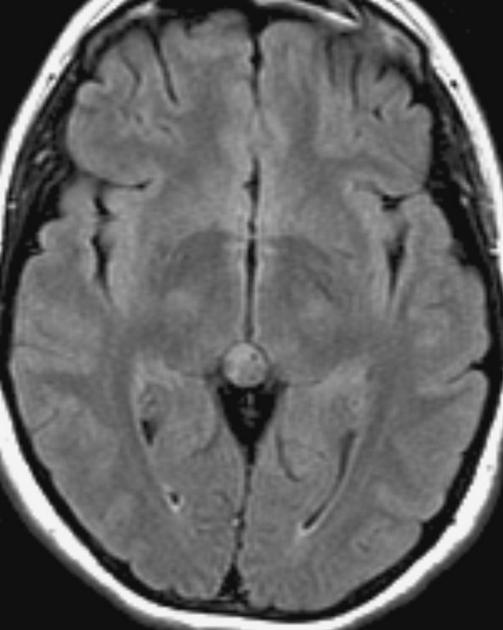
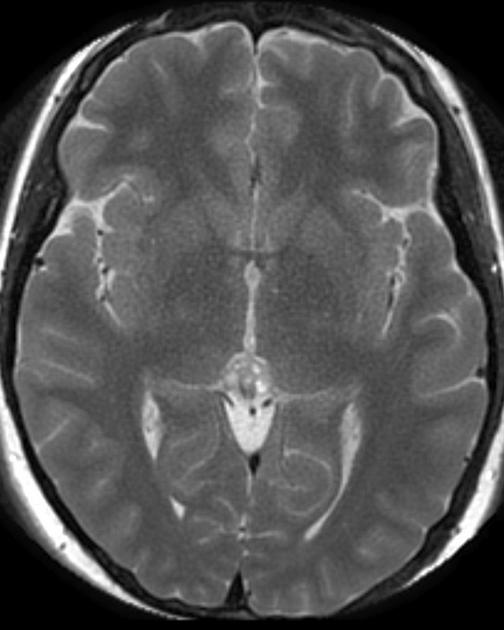
The general workup is MRI with T1/T2 images. Pineoblastomas are generally iso-enhancing on both T1 and T2, but T2 shows cystic components, at times becoming larger than the tumor itself. Surgical resection is treatment which also serves to provide tissue for diagnosis.
|
|
|
|
|
|
General Management and Treatment
Pineocytoma (Grade I)
This is generally treated like a low grade glioma. Surgery is the mainstay treatment via an occipital transtentorial or infratentorial supracerebellar approach, with MRI and fMRI assistance. If complete resection is accomplished, then PFS is 90% - 100% and no further treatment is indicated. With lesser resection, they do worse. In this setting, radiation therapy is more often recommended. If there is residual disease, the target volume is the residual GTV+1.5 cm margin to 50 - 55 Gy, with a resulting OS of 60% - 90% at 5 years.
Intermediate Grade Pineal Parenchymal Tumors
These tumors are rare, and optimal management is not fully explored. Generally, post-operative RT is recommended by some, but not by others. Some of those who do recommend treatment recommend CSI plus boost due to the seeding potential of the CNS. UCSF does not make a 3 category distinction but classifies pineal tumors as either grade I or Grade III for treatment purposes. Those who do recommend treatment treat as for pineoblastoma.
Pineoblastoma
Pineoblastomas are highly malignant tumors composed of patternless sheets of densely packed "small round blue cells." They most frequently affect infants and very young children, who present with increased head circumference or short duration signs and symptoms of increased ICP. MRI imaging shows multi-lobulated heterogeneously enhancing lesions with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage. Infiltration of surrounding structures is common. Leptomeningeal spread is seen in as many as 50% at diagnosis.
Surgery is difficult and complete resections are frequently not possible. Post-operatively children older than 3 are treated with CSI and chemotherapy similar to high risk medulloblastoma and sPNETs. 5 year survival is 50% - 70%, but infants treated with chemotherapy but without radiation do poorly. POG/CCG (now COG) prospectively studied this and found that all tumors recurred within the first 11 months to 1.2 years. All patients died of progressive disease. More aggressive treatment is necessary. Patients with familial bilateral retinoblastoma with pineoblastoma ("tri-lateral retinoblastoma") also have an extremely poor prognosis, with most dying within a year of diagnosis.
Radiation Therapy Treatment Planning And Techniques
Treatment of pineoblastoma is as for medulloblastoma. CSI is delivered post-operatively, to a total dose of 36 Gy at 1.8 Gy/day. If vincristine is given, then reduce the CSI dose to 23.4 Gy, followed by a tumor directed boost to the original disease GTV+1-1.5 cm margin.
Outcomes, Patterns of Failure, Prognostic Indicators
If CSI is omitted then the outcome is poor. With CSI + boost (± SRS boost to residual disease) outcomes are better with 50% - 70% OS5 and mean time to progression 11-12 months.